Plantomycin powerful introduction for plant protection, Plantomycin is a well-recognized antibiotic used in agriculture for plant protection, particularly in India. As the agricultural sector faces numerous challenges due to climate variability, pest infestations, and diseases, Plantomycin has emerged as a powerful tool in preventing bacterial and fungal infections in crops. This antibiotic has gained prominence due to its effectiveness, broad-spectrum application, and adaptability to the Indian environment, where agriculture forms a crucial part of the economy and rural livelihoods. Below is an in-depth exploration of Plantomycin’s features, usage, benefits, and application methods that make it a go-to product for plant protection.
1. What is Plantomycin?
Plantomycin is an antibiotic widely used in agriculture to control bacterial and fungal infections in plants. It contains Streptomycin sulfate, which belongs to the aminoglycoside class of antibiotics. Its primary function is to inhibit the growth of pathogens by disrupting protein synthesis within bacterial cells. Due to its broad-spectrum action, Plantomycin is effective against a variety of bacterial and fungal plant diseases, making it a valuable product in the Indian agricultural landscape. If you want to buy Plantomycin 15g click here now.
2. Mode of Action
Plantomycin works by interfering with the protein synthesis in bacteria and fungi. It binds to the 30S ribosomal subunit in the pathogen’s cells, preventing the assembly of proteins that are essential for the organism’s survival and replication. As a result, Plantomycin inhibits the growth and multiplication of bacteria and fungi, ultimately leading to their death. This mechanism allows it to effectively control infections before they spread and damage crops.
3. Target Diseases
Plantomycin is known for its versatility in treating various bacterial and fungal diseases that affect crops in India. Some of the key diseases it targets include:
- Bacterial Blight: Common in rice and cotton crops, this disease is caused by Xanthomonas bacteria and can lead to significant yield losses.
- Canker: Affecting citrus fruits, canker is a highly destructive bacterial disease that causes lesions on leaves, stems, and fruits.
- Wilt Diseases: These affect a wide range of crops, including tomatoes, eggplants, and chili plants, and are caused by bacterial or fungal pathogens that invade plant vascular systems, leading to wilting and plant death.
- Leaf Spots: Common in vegetables like beans and potatoes, leaf spots are caused by various bacteria and fungi, leading to lesions and defoliation.
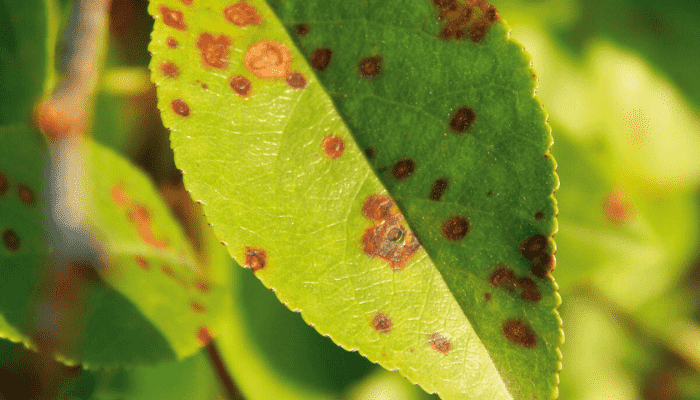

- Soft Rot: Affecting vegetables like carrots, onions, and potatoes, this bacterial disease causes tissue decay and rotting of the produce.
4. Plantomycin Benefits of Using
Broad-Spectrum Action: Plantomycin is effective against a wide range of bacterial and fungal diseases, making it a versatile solution for plant protection across different crops.
Systemic Effect: Once applied, Plantomycin is absorbed by the plant and moves through its vascular system, providing internal protection from bacterial infections. This systemic action ensures that both the treated and surrounding parts of the plant are protected from pathogens.
Environmentally Friendly: When used properly, Plantomycin is safe for the environment. Unlike many chemical fungicides or pesticides, it does not persist in the soil or water and is broken down by natural processes.
Increases Crop Yield: By effectively controlling disease, Plantomycin helps in maintaining plant health, reducing crop losses, and increasing overall productivity. This is especially important in a country like India, where agriculture is the backbone of the economy.
Compatible with Other Treatments: Plantomycin can be used in combination with other fungicides or insecticides, making it part of an integrated pest management (IPM) approach, which is highly recommended for sustainable agriculture.
5. Application of Plantomycin in Indian Agriculture
The effectiveness of Plantomycin largely depends on its correct application. Here’s a detailed guide on how to use it effectively in Indian agricultural settings:
Dosage and Preparation
Plantomycin is typically available in water-soluble powder form, making it easy to mix and apply. The recommended dosage may vary depending on the crop and disease, but a common preparation is 100 to 200 ppm (parts per million), which means dissolving 10 to 20 grams of Plantomycin in 10 liters of water. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for specific dosages.
Application Methods
- Foliar Spraying: The most common method of applying Plantomycin is through foliar spraying. This involves spraying the solution directly onto the plant’s leaves and stems to prevent or control bacterial and fungal infections. The solution should be applied evenly, ensuring full coverage of the plant’s surface.
- Soil Drenching: In some cases, Plantomycin can be applied as a soil drench. This is particularly useful for treating diseases that affect the roots or base of the plant, such as wilt diseases. The solution is poured directly onto the soil around the base of the plant to allow for root absorption.
- Seed Treatment: Plantomycin used for also be used as a seed treatment before sowing. This helps to prevent seed-borne diseases, ensuring healthier germination and growth of crops.
Frequency of Application
The frequency of Plantomycin application depends on the severity of the disease and the crop being treated. For preventive measures, one application during the early stages of plant growth may be sufficient. However, in cases of active infections, repeated applications at intervals of 7 to 14 days may be necessary to completely eradicate the disease.

6. Precautions When use of plantomycin
Although Plantomycin is generally safe for use, it is important to follow certain precautions to avoid any negative effects:
- Avoid Overuse: Overapplication of Plantomycin can lead to resistance in bacterial and fungal populations. This is particularly important to consider, as resistance can render the treatment ineffective over time. Therefore, it is advisable to rotate Plantomycin with other products or biological treatments to reduce the likelihood of resistance development.
- Protective Gear: Always wear protective gear, including gloves and a mask, while mixing and applying Plantomycin to avoid skin or inhalation exposure.
- Follow Local Guidelines: Different regions in India may have specific guidelines or restrictions regarding the use of antibiotics in agriculture. It is important to adhere to these regulations to ensure compliance with environmental and health standards.
7. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) with Plantomycin
To achieve sustainable plant protection, it is highly recommended to use Plantomycin as part of an Integrated Pest Management (IPM) strategy. IPM emphasizes the combination of biological, cultural, mechanical, and chemical methods to control pests and diseases in a balanced way. Plantomycin can be integrated into this system by:
- Combining it with biological control agents such as beneficial microbes that naturally suppress pathogens.
- Using resistant crop varieties alongside Plantomycin to minimize disease outbreaks.
- Implementing crop rotation and sanitation practices to reduce the buildup of pathogens in the soil.
8. FAQ
1.What is Plantomycin?
Ans: Plantomycin is an antibiotic-based plant protection product, primarily used to combat bacterial and fungal infections in crops. It contains Streptomycin sulfate, which inhibits protein synthesis in pathogens, helping protect plants.
2. What is plantomycin technical name?
Ans: The technical name for Plantomycin is a combination of streptomycin sulfate and tetracycline hydrochloride.
3. Plantomycin how to use?
Ans: Plantomycin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic bactericide used to control bacterial diseases in plants. It’s a fine powder that’s fully soluble in water. Mix 0.5–0.75 grams of Plantomycin per liter of water. Spray the mixture evenly on the foliage and infected plant parts.
4. What is the plantomycin dosage per litre of water?
Ans: Plantomycin 0.5 gm – 0.75 gm per liter of water and spray on foliage and infected plant parts.
5. How does Plantomycin work?
Ans: Plantomycin disrupts the protein synthesis in bacterial and fungal cells by binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit, halting the growth and multiplication of harmful pathogens.
6. What plantomycin antibiotics for plant disease control?
Ans: It is effective against a variety of plant diseases, including bacterial blight, citrus canker, wilt diseases, soft rot, and leaf spot, making it useful across many crops.
7. Is Plantomycin safe for plants in Indian climates?
Ans: Yes, Plantomycin is highly adaptable and effective in India’s diverse agricultural climates, particularly in regions where bacterial diseases are prevalent.
8. How is Plantomycin applied to plants?
Ans: It is typically applied as a foliar spray, soil drench, or seed treatment, depending on the crop and the nature of the infection.
9. What crops benefit most from Plantomycin?
Ans: Crops like rice, citrus fruits, tomatoes, chilies, and vegetables such as carrots and potatoes benefit from Plantomycin’s disease-fighting properties.
10. How often should Plantomycin be applied?
Ans: For active infections, it is recommended to apply it every 7 to 14 days. Preventive treatments may require only one or two applications.
11. Can Plantomycin be used in combination with other treatments?
Ans: Yes, Plantomycin can be integrated with other fungicides and insecticides as part of an Integrated Pest Management (IPM) strategy.
12. Does Plantomycin require safety precautions?
Ans: Yes, users should wear protective gear, follow dosage instructions, and avoid overuse to prevent resistance.
13. Is Plantomycin environmentally friendly?
Ans: When used responsibly, Plantomycin has a minimal environmental impact and does not persist in the soil.
14. How much is Plantomycin Price?
Ans: The price of Plantomycin can vary depending on the retailer and region. For the most accurate pricing, it’s best to check local agricultural supply stores or online marketplaces.Plantomycin 15g Price is ₹50 to ₹100. You can Plantomycin 15g buy by clicking this link in the best offer price.
9. Conclusion
Plantomycin is a powerful and effective solution for combating bacterial and fungal diseases in plants, particularly in the Indian agricultural context. Its broad-spectrum action, systemic nature, and compatibility with other treatments make it a valuable asset for farmers. When used responsibly, Plantomycin helps increase crop yields, promotes healthy plant growth, and ensures sustainable agriculture practices.


